Stopped having periods.
Whos's at risk?
What causes abnormal vaginal bleeding and who is at risk? Abnormal vaginal bleeding may occur between the normal menstrual bleeds (intermenstrual bleeding)or it may take the form of unusually heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia). In postmenopausal women, it may develop after a number of years without any vaginal bleeding.
It's inportant to understand exactly what is causing the bleeding and where it's coming from (uterus, vagina, or some other organ or tissue) and to make decisions about how to control or stop the bleeding.
A wide range of "normal" menstrual periods Periods differ from woman to woman and from month to month. A period can last from three to 10 days, and occur every three to six weeks. This pattern can vary with age, stress, diet, exercise and inherited factors. The flow can also vary. Around 40ml (two tablespoons) of fluid is lost, which the body quickly replaces.
It is common for women to suffer some cramping pain with their period. This is felt just below the navel and may spread ito the legs or lower back. It can be felt as a dull ache or sharp twinge. During a period, it is also common to feel bloated and heavy, get more pimples, feel tense and emotional, and have sore breasts and greasier hair.
What gynaecologic conditions are associated with irregular vaginal bleeding?Irregular vaginal bleeding is a possible sign or symptom of a range of causes. For others, the cause depends on their age and the site of bleeding. Once pregnancy has been ruled out, some of the known causes include:
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- Contraception-such as the pill, injection or IUD (intrauterine device)
- Vaginal infections
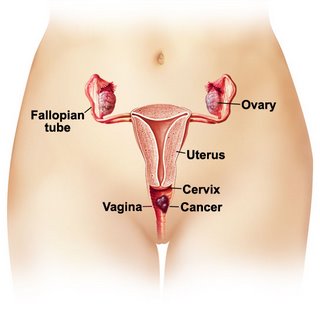
- Tumours, polyps or fibroids of the vagina, cervix, uterus or fallopian tubes
- Cervical disorders-such as cervical ectropion, a condition common among younger women, especially young women taking birth control pills-in which the cervical tissue becomes more susceptible to abrasion, often associated with bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Cancer of the uterus, cervix, vagina or vulva
- Some sexually transmitted diseases, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea or genital warts
- Vaginal injury from trauma or sexual abuse
- Some medications such as anticoagulants or anti-epilepsy drugs
- Underlying health problems such as bleeding or thyroid disorders.Dysfunctional uterine bleedingIn more than half the women with
More about womens - Breast Cancer


1 Comments:
nice blog here is a blog about women health and tubal reversal
http://www.mybabydoc.com/blog/
tubal reversal
Post a Comment
Links to this post:
Create a Link
<< Home